| docs | ||
| packages | ||
| src | ||
| syn_umbrella | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
FastNetMon
Author: Pavel Odintsov pavel.odintsov at gmail.com Follow my Twitter
Join to maillist Look at road map
License: GPLv2
FastNetMon - A high performance DoS/DDoS load analyzer built on top of multiple packet capture engines (NetFlow, IPFIX, sFLOW, netmap, PF_RING, PCAP).
What can we do? We can detect hosts in our own network with a large amount of packets per second/bytes per second or flow per second incoming or outgoing from certain hosts. And we can call an external script which can notify you, switch off a server or blackhole the client.
- Binary rpm packages for CentOS 6/7 and Fedora 21
- Automatic install script for Debian/Ubuntu/CentOS/Fedora
- Manual install on FreeBSD and Dragonfly BSD
- Manual install on Mac OS X
- Manual install on Slackware
- You could order VPS with preinstalled FastNetMon: http://vps2fast.com/vds/
Supported protocols:
- NetFlow v5, v9
- IPFIX
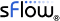 v5
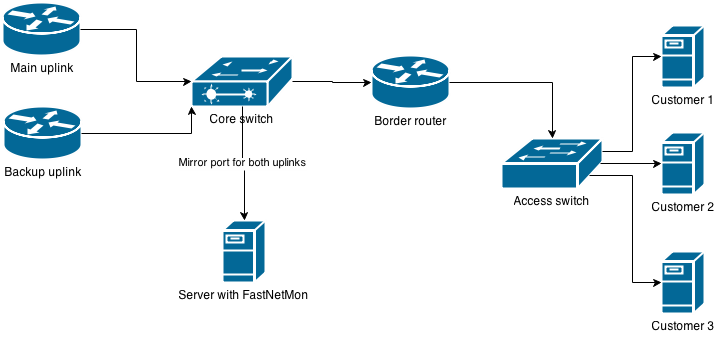
v5- Port mirror/SPAN capture with PF_RING (with ZC/DNA mode support need license), NETMAP and PCAP
Features:
- Can process incoming and outgoing traffic
- Can trigger block script if certain IP loads network with a large amount of packets per second
- Can trigger block script if certain IP loads network with a large amount of bytes per second
- Can trigger block script if certain IP loads network with a large amount of flows per second
- netmap support (open source; wire speed processing; only Intel hardware NICs or any hypervisor VM type)
- Supports L2TP decapsulation, VLAN untagging and MPLS processing in mirror mode
- Can work on server/soft-router
- Can detect DoS/DDoS in 1-2 seconds
- Tested up to 10GE with 5-6 Mpps on Intel i7 2600 with Intel Nic 82599
- Complete plugin support
Supported platforms:
- Linux (Debian 6/7, CentOS 6/7, Ubuntu 12+)
- FreeBSD 9, 10, 11
- Mac OS X Yosemite
What is "flow" in FastNetMon terms? It's one or multiple udp, tcp, icmp connections with unique src IP, dst IP, src port, dst port and protocol.
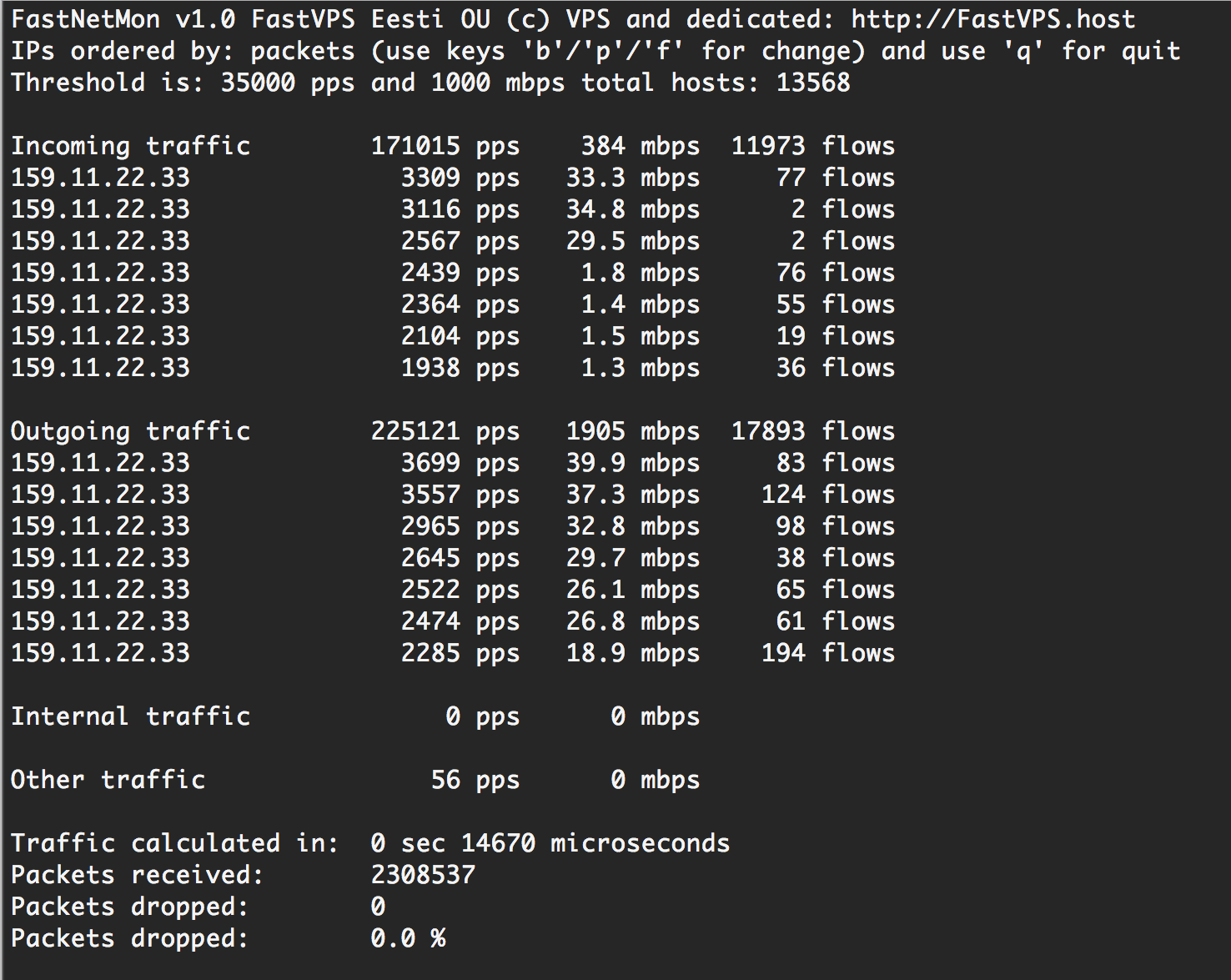
Main program screen image:
Example for cpu load on Intel i7 2600 with Intel X540/82599 NIC on 400 kpps load:

Example of first notification:
subject: Myflower Guard: IP xx.xx.xx.xx blocked because incoming attack with power 120613 pps
body:
IP: XX.XX.XX.XX
Initial attack power: 98285 packets per second
Peak attack power: 98285 packets per second
Attack direction: outgoing
Incoming traffic: 62 mbps
Outgoing traffic: 65 mbps
Incoming pps: 66628 packets per second
Outgoing pps: 98285 packets per second
Incoming flows: 16
Outgoing flows: 16
Incoming
UDP
xx.xx.xx.xx:33611 < 216.239.32.109:53 729021 bytes 5927 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:33611 < 216.239.34.109:53 231609 bytes 1883 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:33611 < 216.239.36.109:53 728652 bytes 5924 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:33611 < 216.239.38.109:53 414387 bytes 3369 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:42279 < 216.239.34.109:53 248091 bytes 2017 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:42279 < 216.239.36.109:53 737508 bytes 5996 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:42279 < 216.239.38.109:53 321276 bytes 2612 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:51469 < 216.239.32.109:53 735663 bytes 5981 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:51469 < 216.239.34.109:53 237267 bytes 1929 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:51469 < 216.239.36.109:53 735663 bytes 5981 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:51469 < 216.239.38.109:53 318570 bytes 2590 packets
Outgoing
UDP
xx.xx.xx.xx:33611 > 216.239.32.109:53 531309 bytes 6107 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:33611 > 216.239.34.109:53 531222 bytes 6106 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:33611 > 216.239.36.109:53 531222 bytes 6106 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:33611 > 216.239.38.109:53 531222 bytes 6106 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:51469 > 216.239.36.109:53 532701 bytes 6123 packets
xx.xx.xx.xx:51469 > 216.239.38.109:53 532788 bytes 6124 packets
Example of second notification:
subject: Myflower Guard: IP xx.xx.xx.xx blocked because incoming attack with power 120613 pps
body:
IP: xx.zz.xx.1
2014-11-21 08:01:11.419798 216.239.32.109:53 > xx.xx.xx.xx:38458 protocol: udp flags: size: 123 bytes
2014-11-21 08:01:11.419799 216.239.32.109:53 > xx.xx.xx.xx:38458 protocol: udp flags: size: 123 bytes
2014-11-21 08:01:11.419816 xx.xx.xx.xx:51469 > 216.239.36.109:53 protocol: udp flags: size: 87 bytes
2014-11-21 08:01:11.419837 216.239.38.109:53 > xx.xx.xx.xx:33611 protocol: udp flags: size: 123 bytes
2014-11-21 08:01:11.419838 216.239.34.109:53 > xx.xx.xx.xx:33611 protocol: udp flags: size: 123 bytes
2014-11-21 08:01:11.419859 216.239.38.109:53 > xx.xx.xx.xx:42279 protocol: udp flags: size: 123 bytes
2014-11-21 08:01:11.419929 216.239.38.109:53 > xx.xx.xx.xx:33611 protocol: udp flags: size: 123 bytes
2014-11-21 08:01:11.419961 216.239.32.109:53 > xx.xx.xx.xx:38458 protocol: udp flags: size: 123 bytes
2014-11-21 08:01:11.419962 216.239.32.109:53 > xx.xx.xx.xx:38458 protocol: udp flags: size: 123 bytes
2014-11-21 08:01:11.419963 216.239.32.109:53 > xx.xx.xx.xx:38458 protocol: udp flags: size: 123 bytes
2014-11-21 08:01:11.419963 216.239.32.109:53 > xx.xx.xx.xx:38458 protocol: udp flags: size: 123 bytes
To enable sFLOW simply specify IP of server with installed FastNetMon and specify port 6343. To enable netflow simply specify IP of server with installed FastNetMon and specify port 2055.
Why did we write this? Because we can't find any software for solving this problem in the open source world!
How I can help project?
- Test it!
- Share your experience
- Share your improvements
- Test it with different equipment
- Create feature requests